Product Management & Data Science Collaboration
Product Managers drive the success of a product by driving value for its users. They discover what’s most important to the users, then build and ship products catering to their needs. Data Scientists enable product managers to identify user needs, discover pain-points, build effective solutions, and measure the impact of those solutions. The best product managers are always backed by data.
Their decisions are driven by research and data insights rather than intuition and guesswork.
Their decisions are driven by research and data insights rather than intuition and guesswork.
Whenever product managers want to drive product changes, they wouldn’t just pitch the idea to the leadership and start working on it. Instead, they dig into the historical data to identify insights that can support their hypothesis. This helps target efforts on initiatives that directly address user pain-points. It ensures every product change shipped out provides a positive experience to the user and drives key business goals.
How collaboration drives successful products?
A strong collaboration between product managers and data scientists can drive successful products. Let’s look at some ways this collaboration can help:
a. Get rid of opinion-based decisions
Opinions can be subjective. What might seem like a good decision to one might not seem like a good decision to another person, so there is a lot of subjectivity. Without data, the opinion of the highest-paid person can impact product decisions - typically known as HIPPO (highest paid-person’s opinion). Data provides an objective measure that everyone can align on.
b. Understand user journey
Data can serve as a source of truth for the voice of the users. Product Managers get an improved sense of what their users want, what their experience with the product is, and how they can improve the product for the users. A great way to understand users is by analyzing their journeys on the product. Here are examples of key questions that can be answered through data:
What features of the product do users most engage with?
At what point in the product do you notice the highest bounce rate?
What is the average time between key user actions?
What percentage of the users come back to use the product in X days? And many more…
c. Prioritize initiatives
Making product changes based subjectively can result in a lot of wasted effort. Data helps identify the highest-impact changes that can truly address user needs. Based on information about user habits and preferences, any new ideas can be classified as ‘must-haves’ vs ‘nice-to-haves’. This segregation can help prioritize ideas and align large teams towards a common goal. In addition, data-driven insights can avoid building features which users don’t need, thus avoiding feature overload.
d. Align teams
Data can be a powerful lever to influence stakeholders and align them towards a shared goal. Product data is critical to the success of the org and is used by cross-functional teams to drive operations and strategy. This can also help with resource allocation on high-value product launches. Often cross-functional products can involve working closely with Sales teams, Marketing Teams, or Research Teams. Each team might have different priorities. Data can serve as a common baseline for product managers to influence key stakeholders and drive decision-making.
Commonalities between the roles
a. Product & business knowledge
b. Stakeholder Management
c. Customer obsession
d. Data Intuition
Let’s look into some similarities between the two domains. Problem identification and solution ideation require a deep understanding of the product and revenue model. Without a strong product sense, data scientists can find it difficult to derive actionable insights from the data that really help the users. Similarly, without a strong product sense, product managers can have a hard time ideating and prioritizing the right features to build. A common goal for both teams should be to understand their users, so they can ask the right questions.
b. Stakeholder Management
Ideating, building, and shipping products often involves a lot of different stakeholders. Design, Engineering, Marketing, etc may be involved at different stages of the feature launch. Being able to work in a cross-functional environment and influence people at different levels of the organization is a key skill. Both data scientists and product managers can highly benefit by engaging with stakeholders and getting them onboard with their ideas and plan. Together, they can create products that are data-driven and ensure every change rolled out is a positive step towards the larger business goals.
c. Customer obsession
Customer obsession places a focus on creating better experiences for the users. It is a commitment to having a customer-first approach, and requires an obsession with data. It has rightly been said - ‘if you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it’. For product-led companies, it is extremely important to make customers' needs and expectations a priority across the business. Gather direct and indirect feedback from the users and understand what keeps them coming back to you.
A focus on the consumer builds brand loyalty and generates customer trust so they continue to seek out your business and recommend it to others. By putting the customer first, data scientists can use technical skills to understand what drives their behavior, and product managers can prioritize features that provide experiences that customers seek.
A focus on the consumer builds brand loyalty and generates customer trust so they continue to seek out your business and recommend it to others. By putting the customer first, data scientists can use technical skills to understand what drives their behavior, and product managers can prioritize features that provide experiences that customers seek.
d. Data Intuition
While Product managers are not expected to be hands-on with data, it is essential to have a high data literacy and a strong data sense. A data-driven product manager should know enough about the data to ask the right questions to the data team. They should also value data enough to make decisions based on data instead of their intuition. Additionally, being data-driven can help product managers quickly gather basic insights and share insightful stories with the larger audience.
Common instances of ineffective collaboration:
We noticed some common mistakes that can negatively impact the collaboration between data and product teams. Let’s understand them so we can proactively avoid them.
b. Using data only to validate product ideas
c. Failing to communicate
a. Involving data team too late
A lot of product teams consider data science teams as their ‘experimentation partners’ and loop them in when they have to measure the impact of feature changes. But data teams can add a lot of value in identifying the high-value opportunities, finding patterns in customer feedback, and deriving insights from user journeys. Working closely with them at every step of the product life cycle can be a great value-add.
b. Using data only to validate product ideas
Data should be used from the start to guide product direction. A common mistake product managers make is to rely on data science teams only to pull some numbers and query the database to validate selected product ideas. A successful collaboration is when data teams are involved in product strategy and their insights are used to drive product and experimentation roadmap.
c. Failing to communicate
Keep the teams updated on key milestones, success criteria, and business goals. Communicate wins and failures with the larger audience. Track the right metrics, measure success, and document learnings from the failures.
How to drive this collaboration effectively:
Now that we understand the importance of collaboration and their shared space and skill sets, let us now understand how collaboration can be made effective through some of the best practices.
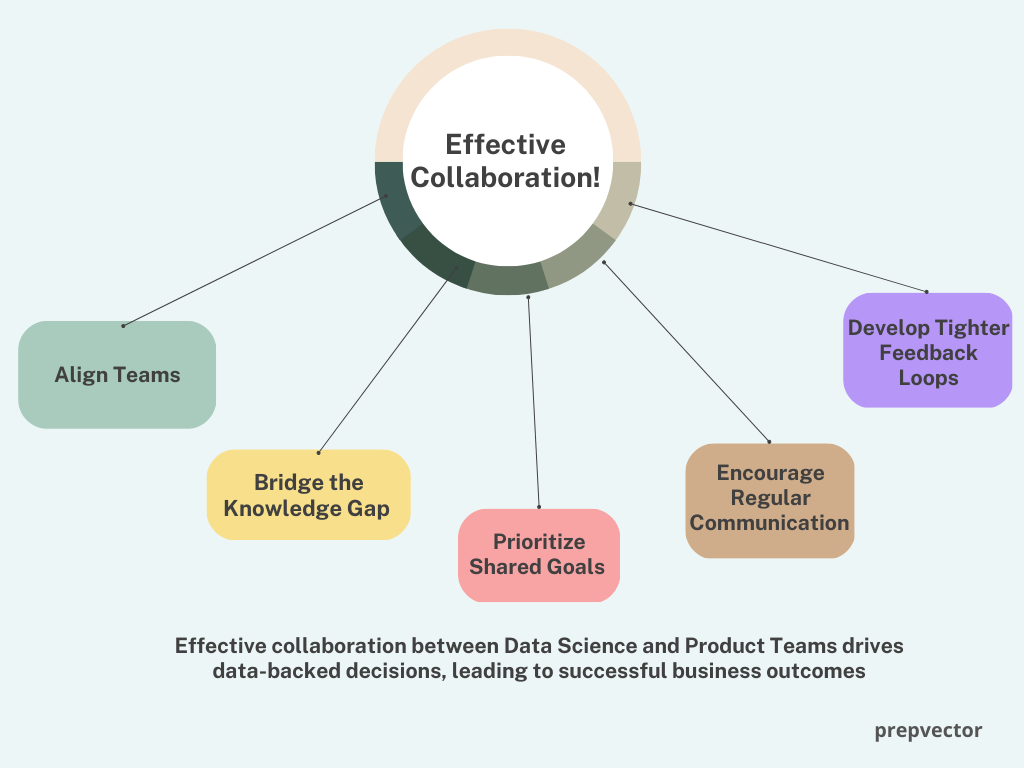
1. Align Teams
Effective collaboration can flourish when there is alignment between the teams. Product Managers need to involve data teams early on. From ideation, execution, measurement, and iteration - data can build confidence in the product decisions. Bring the data teams onboard whenever there are changes being made to product vision or execution roadmap. Ensure the teams are aligned on the product strategy, roadmap, goals, and product metrics.
2. Bridge the Knowledge Gap
Encourage knowledge sharing between data and product teams to provide a greater perspective about each role. Product Managers should be encouraged to develop a ‘data sense’ - understand how the user journey is captured and recorded through various data points and have a learning mindset to the techniques used by data scientists to derive insights. Data Scientists should be encouraged to develop a ‘product sense’ - understanding the product goals, target audiences, and growth levers can help data scientists derive insights that are actionable by the product teams.
3. Prioritize Shared goals
The best collaboration between teams flourish when there is a shared goal of improving products and a firm conviction that learning from the users is the best way to meaningfully build products. Data can truly help uncover what the users want and what their experience is with the product. Collaboration works best when the roles are divided but not separate. What this means is that at all times there should be complete alignment between the product manager and the data scientist on the common goal, in a way that even when working in isolation their efforts complement each other.
4. Encourage Regular Communication
Regular communication reduces friction between teams. It is of utmost importance to have a clear understanding of the shared goals. Keep the data teams in loop if there are any changes to the strategy, roadmap or if there are new feature launches being planned. Weekly meetings and shared trackers can keep the teams aligned and focused. It also ensures the efforts are focused in the right direction and keeps everyone updated in case of issues or high-priority action items.
5. Develop Tighter Feedback Loops
Allow for ideas and feedback to be shared early and regularly, ensuring full alignment along the way and preventing sunk cost fallacy issues. Maintain transparency and be open to feedback. Encouraging tighter feedback loops between data and product teams leads to faster time to iteration of product ideas. It also allows for failures to be communicated respectfully and be learnt from. This partnership enables product teams to experiment with multiple features so they can ship a feature that matches user needs and improves the product experience.
Data scientists and product managers are key players in the field of data-driven decision-making. Collaboration is an important part of a company’s success because it helps them take data-driven decisions, which leads to better products for their customers.
A Product Manager can amplify their impact by leveraging data to build products and prioritize changes. They can also develop a deeper understanding of metrics that can keep a tab of the overall health of the product. Data Scientists can provide actionable insights to product teams and build experiments to measure the impact of product updates. This collaboration can highly benefit the organization as both teams learn to speak each other's language.
By integrating product and data, you are adopting a cultural change. You’re trying to get people to change how they think about moving from ideas into features, how they evaluate decisions and how strive for success. It will shift how decisions are made. Data-driven products will improve user experience, drive long-term retention, and contribute to business outcomes.
Check out our course Master Product Data Science, an 8 week comprehensive course to upscale your career with us!

Copyright © 2022
Contact Us!
Got a question? Reach out to us and we will get back to you ASAP!
Thank you!
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
By submitting this form, you consent to abide by the Privacy Policy outlined by PrepVector.
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
Access has ended, sorry.
But you can reach out to us at operations@prepvector.com if you need access to the giveaway.
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
By submitting this form, you consent to abide by the Privacy Policy outlined by PrepVector.
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
By submitting this form, you consent to abide by the Privacy Policy outlined by PrepVector.

