Skills of a Product Manager
The key to success in any role is twofold:
1) possessing the skills needed
2) effective implementation of those skills.
1) possessing the skills needed
2) effective implementation of those skills.
It is no less different when it comes to an efficient product manager. An APM is a master of hard and soft skills that are required to drive the team and build success. The highly sought-after PMs are the ones who understand and implement the appropriate skills required while working with their multi-faceted job demands.
A product manager is responsible for building great products, strategizing their launch, measuring their health, and designing a marketing strategy for it as part of the product lifecycle. This often requires a combination of multiple skills - customer obsession, decision-making, collaboration, leadership, to name a few. Product managers often have to drive cross-functional projects, which need them to have fair technical competence and good communication skills.
Whether you are just starting out in product management or want to advance your career in this domain, here are the key skills you will need to be effective in your role:
Whether you are just starting out in product management or want to advance your career in this domain, here are the key skills you will need to be effective in your role:
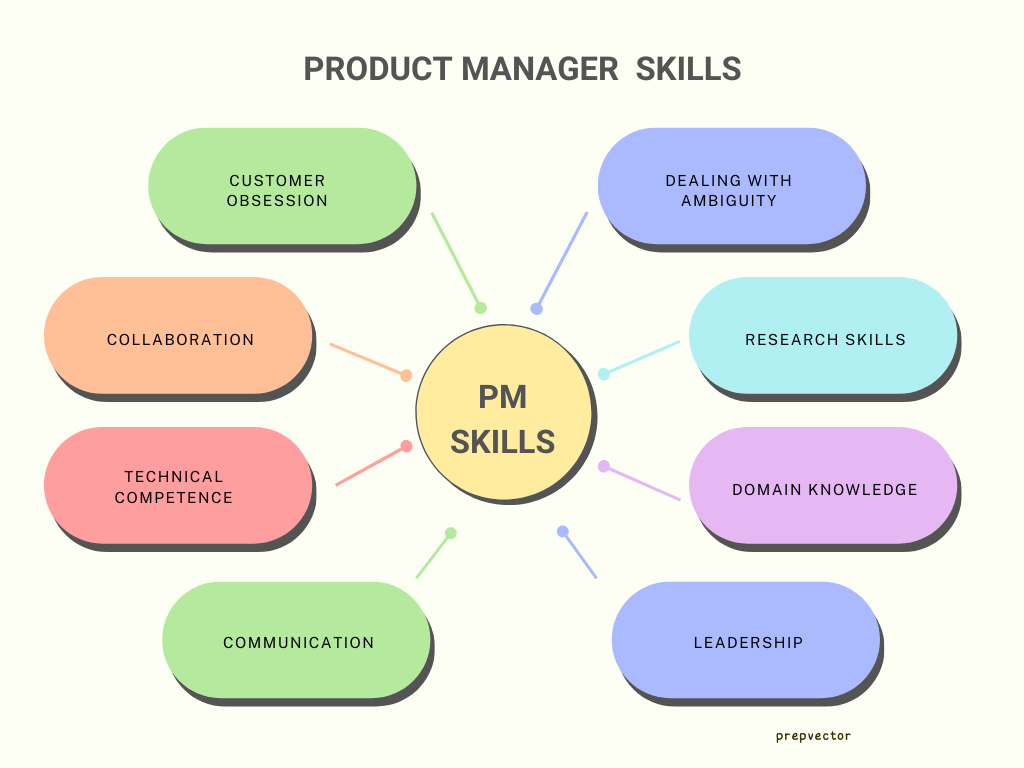
1. Customer Obsession
Great products are built keeping the customer's needs and pain points in mind. They solve important customer problems. Building an affable product requires a product manager to understand the user’s needs and expectations. This makes it critical to evaluate how users are interacting with the product. This can be done in several ways - user-focused research studies, surveys, or diving into user interaction data. With proper analysis of the findings from each of these, a PM needs to develop a deep understanding of the customer and use it to build/improve their products. To understand customer obsession, there are many follow-ups that companies do to understand their customers. Like product feedback and reviews, surveys, etc. With proper analysis of the responses received from the users, developing beneficial and satisfactory products for their customers will be much easier and more positive.
2. Collaboration
Product managers often collaborate with multiple teams - engineering, data science, marketing, legal, etc.—to develop great products. They create an action plan and align everyone to work towards a common goal. This facet of the role is also known as "collaborative product management," where the PM plans, coordinates, controls, and monitors the progress that is delegated across departments.
3. Decision Making
Product managers often have to make decisions very early on in the product development lifecycle and sometimes with limited information. The chances of seeing a red flag early on in the development stage are low. The decisions can involve the release of new features, an improvement to existing ones, or financial or resource-allocations. Hence, the right decisions will always save time and money. This particular skill might sound very simple and easy, but in reality, it is not. Because the decision reveals itself, whether it is good or not, only at the end. To make this process, to some extent, error-free, it is advisable to keep everyone aligned about the product and processes, including the team members, while discussing the non-confidential details of the process or product. It is also a chance to evaluate diverse ideas and ensure the product is an outcome of good decisions. Also, the product is the outcome of all the decisions made, so be vigilant.
4. Technical Competence
Technical competence is a core hard skill that differentiates a great product manager from a good one. Having some technical competence will make the job significantly easier. This is not just limited to software products, but all kinds of products involve some extent of technicality, including logistics, analysis, or experimentation. Because everything that we deal with at present, implicitly or explicitly, involves traces of technology. Be it non-software products, technology is involved when trying to analyze the logistics and statistics of the product's reach in the market. And everyone will agree that logistics and statistics are integral for tracking and improvising. For software products, this becomes even more important. Product managers who understand the basics of code development and analysis stand out and are able to partner with the engineering and data science teams effectively.
5. Dealing with ambiguity / Extensive research skills
Ambiguity often intimidates product managers because they deal with complex product problems. Ambiguity in a product is the presence of more than one interpretation of information, leading to confusion. Hence, dealing with this ambiguity upfront is significant for a product management team. This fallout is majorly due to improper communication. In fact, ambiguity is one of the four pillars that make the working environment and decision-making challenges. These four pillars are summarized as VUCA - part of four that leaves with conflict when a product is developed. Volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity These factors need to be managed at every step in a product manager’s role. Despite taking up less space in the graph, eliminating these four factors makes the attempt to develop the product successful. Therefore, a good product manager always has an eye to ensure that VUCA is shielded and forsaken.
6. Leadership
The quality of a leader defines the success of a team. Leadership is an umbrella term. Under leadership, there are many qualities like vision for the team, fairness, optimism, focus, intuition, and a relentless pace towards growth. When it comes to facing an issue, a good leader will either communicate it to the desired person or provide a real solution to it. Such qualities will motivate and drive the team.
A few more aspects of a good leader are being tactical and strategizing every move. This does not mean having a plan B for every single move. But being able to cope and achieve the desired result by surmounting the obstacles. Great leadership can fuel product development and growth in any organizatio
7. Communication
Misinterpretations are never advocates of growth. Communication is key because often, a PM has to collaborate with multiple teams, deliver presentations to stakeholders, and interact with customers to understand the product usage. They are also responsible for writing product specifications and requirements documents that contain ideas from conceptualization to launch of the product, along with KPI measurement. This document is often referred to by multiple teams that work closely with the product managers. Communication skills also come into play when discussing product initiatives and priorities. It is how a PM will convey their thoughts to the team. Effective communication is defined by ABC, which stands for It should define the ABC of effective communication, which is accuracy, brevity, and clarity. When a conversation meets these factors, there are negligible, less to zero chances of misalignment. An effective way to develop communication skills in product management is to converse with the customers and the team often.
8. Domain Knowledge
Domain knowledge is always dynamic but critical to developing successful products. This means it is essential for a good product manager to be aware of all the recent trends in the market and gather information about competitor products in the market. Knowledge about the current affair in the market will give a flair advantage to spiral up the business of the product because existing trends reflect the customer's priorities.
Getting hooked up with the latest market developments in their domain news around the world will definitely benefit a PM to understand the user preferences and develop business skills to navigate their job much more effectively. ad-hoc trends.
Getting hooked up with the latest market developments in their domain news around the world will definitely benefit a PM to understand the user preferences and develop business skills to navigate their job much more effectively. ad-hoc trends.
9. Others
Apart from the above-mentioned skills, there are also a couple more that will help a PM in the expertise of product management.
Marketing - Marketing is more of a responsibility than a skill that a product manager should be aware of. This skill will help a PM to successfully land his/her product on the market.
UX - User experience or learning the basics of UX will help you design a user interface that your customer is expecting from you. The scalability of the product depends on user interaction with the product, and UX is the bridge.
Product manager jobs require these skills to drive impact at your workplace. Mastering these above-mentioned skills will definitely help you kickstart your product manager career or up-level your role as a PM. If you need a structured coaching plan to help with product and data, check out our courses here!

Copyright © 2022
Contact Us!
Got a question? Reach out to us and we will get back to you ASAP!
Thank you!
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
By submitting this form, you consent to abide by the Privacy Policy outlined by PrepVector.
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
Access has ended, sorry.
But you can reach out to us at operations@prepvector.com if you need access to the giveaway.
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
By submitting this form, you consent to abide by the Privacy Policy outlined by PrepVector.
One more step!
Just a few details before you can download the resources.
Thank you!
Download your resource here
Download your resource here
By submitting this form, you consent to abide by the Privacy Policy outlined by PrepVector.

